Introduction to Scanning Electron Microscopy (Life Sciences)
Summary
The "Introduction to Scanning Electron Microscopy (Life Sciences)" course at ANU's Centre for Advanced Microscopy provides participants with an understanding of SEM operation, sample preparation, optimization for biological imaging, and identification of SEM components.
Date & time
Date/time
9 Oct 2025 | 9am - 5pm
Course type
Course type
Professional short course
Contact
Contact
Call to action
By the end of this course participants are expected to be able to understand:
- how an SEM works
- how to prepare samples for various applications
- how to optimise SEM for biological imaging, and
- identify the various components making up an SEM.
Specific topics covered
- How does the SEM work
- Instrument components
- Signals in the SEM
- Aberrations
- Depth of Field
- Optimising SEM Conditions
- Image Resolution
- Low Voltage SEM
- Sample preparation for biological material including possible artefacts
- Correlative Light and Electron Microscopy (CLEM)
Scanning Electron Microscopes and Electron Microprobe
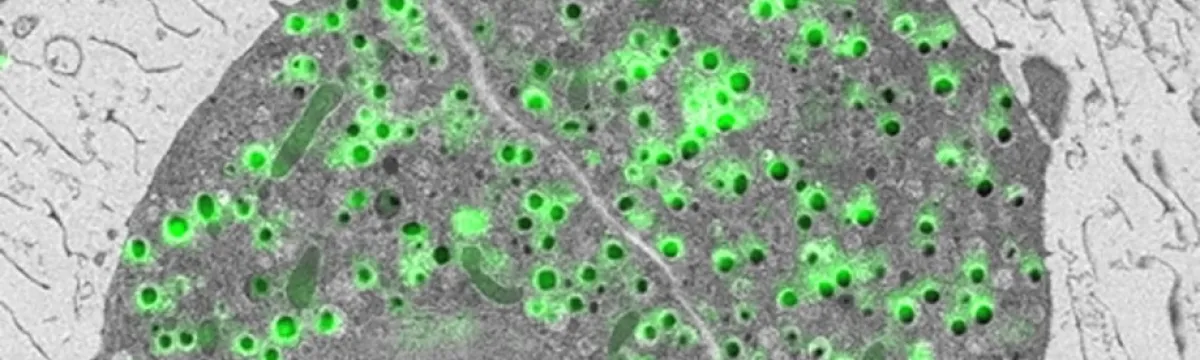
Biological applications of Scanning Electron Microscopy
- Visualisation of external morphological characteristics.
- Visualisation of cellular structure in large view
- Correlative Light and Electron Microscopy (CLEM)
Please register your interest for the next workshop here.
Maximum number of students: 6
Cost
ANU students: AUD$160.00 per person.
Non-ANU students: AUD$286.00 per person ($260 + GST).
